Integration of eQTL and GWAS data on Alzeimer's disease
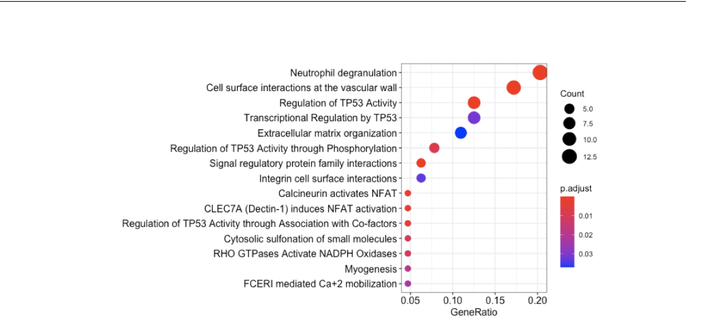
The GWA (Genome-wide Association) studies, when statistically analyzed with expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) studies can provide compelling single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that influence the disease condition which further could be targeted in diagnosis and treatment. eQTL provides the relationship between the various SNP’s and their effect on the gene expression or the disease condition detailed to the locus level. Recent findings show that most GWAS findings overlap with expression expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL), indicating their potential involvement in regulation of gene expression.Mendelian randomization method attempts to predict the causative effect of the SNP on gene expression for a particular disease. Though the MR method is able to find significant SNPs when the variance in the data is high, but also requires a huge sample size to detect the effect of the SNP on the disease. The summary-based mendelian randomization method, thus can be used to test the pleiotropic association between phenotype and gene expression and differentiate the phenomenon with causality. While the heterogeneity in dependent instruments method (HEIDI) provides a clear distinction between linkage and pleiotropy. Thus, with the combination of these statistical tests and analyzing them with differential expression analysis, would provide us an insight as to which of the SNPs and genes are part of the causal module in the pathology of the disease. The research paper is under review currently.